Introduction
Sonography, a vital diagnostic tool in modern medicine, plays a crucial role in healthcare diagnostics.
This section explores the responsibilities and significance of sonographers in the medical field.
Definition of Sonographer
A sonographer is a highly skilled healthcare professional trained in performing ultrasound examinations.
Using specialized equipment, they capture images of internal organs, tissues, and blood flow patterns.
Sonographers work closely with physicians and radiologists to interpret these images, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment planning for various medical conditions.
Importance of Sonographers in Healthcare Industry
Sonographers are indispensable in the healthcare industry due to their expertise in non-invasive imaging techniques.
They help diagnose a wide range of conditions, from pregnancy complications to cardiovascular diseases.
Their ability to produce high-quality ultrasound images enables early detection of abnormalities, facilitating timely medical interventions and improving patient outcomes.
Sonographers also contribute to patient care by providing real-time imaging guidance during procedures such as biopsies or fluid aspirations, enhancing precision and safety.
In obstetrics, sonographers monitor fetal development, detect anomalies, and ensure maternal and fetal health throughout pregnancy.
Their role extends beyond diagnostics to providing emotional support and reassurance to expectant parents.
In cardiology, sonographers assess heart function, detect heart diseases, and monitor the effectiveness of treatments like pacemakers.
They play a pivotal role in managing cardiac health and preventing complications.
In vascular sonography, they evaluate blood flow and detect conditions such as deep vein thrombosis or arterial blockages, crucial for preventing strokes and managing vascular diseases.
Sonographers are at the forefront of technological advancements in ultrasound imaging, continually refining techniques and protocols to enhance diagnostic accuracy and patient comfort.
Their interdisciplinary collaboration with healthcare teams underscores their role as key contributors to comprehensive patient care strategies.
Basically, sonographers are integral to modern healthcare, blending technical expertise with compassionate patient care.
Their skill in ultrasound imaging not only aids in diagnosing diseases but also supports treatment decisions, making them indispensable allies in the quest for better health outcomes.
By understanding the multifaceted responsibilities and importance of sonographers, we appreciate their significant impact on medical practice and patient well-being.
What Does a Sonographer Do? Key Responsibilities
Sonographers play a crucial role in healthcare, using specialized equipment to perform diagnostic imaging procedures.
This profession requires specific educational paths, training, and certification to ensure proficiency across various specialized areas.
Educational Requirements
Becoming a sonographer typically requires at least an associate degree in sonography or a related field.
Some positions may prefer or require a bachelor’s degree for advanced roles or specialization.
Coursework often includes anatomy, physiology, medical terminology, and ultrasound physics.
Training and Certification Needed
After completing educational requirements, aspiring sonographers must undergo clinical training. This hands-on experience is essential for developing skills in ultrasound imaging techniques and patient care.
Certification is often required and can be obtained through organizations such as the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) or the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT).
Specialized Areas Within Sonography
Sonography offers various specialized areas, each focusing on different aspects of diagnostic imaging:
- Cardiac Sonography: Involves imaging of the heart and blood vessels, assessing cardiac function and detecting abnormalities such as heart disease.
- Vascular Sonography: Focuses on imaging blood vessels to evaluate blood flow and detect conditions like blood clots or arterial disease.
- Abdominal Sonography: Includes imaging of organs in the abdomen, such as the liver, kidneys, and pancreas, aiding in the diagnosis of conditions like gallstones or tumors.
Sonographers may also specialize in obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN) sonography for imaging the female reproductive system and monitoring fetal development during pregnancy.
Generally, sonographers play a vital role in healthcare by providing detailed images that aid in diagnosing and treating medical conditions.
The path to becoming a sonographer involves rigorous education, hands-on training, and certification in specialized areas such as cardiac, vascular, or abdominal sonography.
These professionals contribute significantly to patient care through their expertise in diagnostic imaging techniques.
This concise overview highlights the educational journey, training requirements, and specialized areas within the field of sonography, emphasizing the importance of skilled professionals in delivering high-quality healthcare services.
Transform Your Career Today
Unlock a personalized career strategy that drives real results. Get tailored advice and a roadmap designed just for you.
Start NowRead: Licensing and Certification for Genetic Counselors
Key responsibilities of a sonographer
Sonographers play a crucial role in the healthcare field, utilizing advanced imaging technology to diagnose and monitor various medical conditions.
Their responsibilities encompass a range of tasks that are vital for accurate patient diagnosis and treatment planning.
Performing Diagnostic Medical Sonograms
Sonographers perform diagnostic medical sonograms, also known as ultrasound scans, using specialized equipment that emits high-frequency sound waves.
These waves create real-time images of internal organs, tissues, and blood flow within the body.
By capturing detailed images, sonographers assist physicians in evaluating and diagnosing medical conditions such as pregnancy complications, cardiovascular diseases, and abdominal disorders.
Analyzing Images and Data
After obtaining sonographic images, sonographers analyze them to assess the health and functionality of organs and tissues.
They interpret the images to identify abnormalities, such as tumors, cysts, or structural anomalies.
This analytical process requires a keen understanding of anatomy, physiology, and pathology to accurately recognize and differentiate between normal and abnormal findings.
Communicating Findings to the Medical Team
Effective communication is crucial in the role of a sonographer.
Upon analyzing the images and data, sonographers prepare detailed reports summarizing their findings.
They communicate these findings to the medical team, including physicians and other healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care.
Clear and precise communication ensures that accurate diagnoses are made and appropriate treatment plans are implemented in a timely manner.
Collaborating with Healthcare Professionals
Sonographers collaborate closely with radiologists, cardiologists, obstetricians, and other specialists to provide comprehensive patient care.
They discuss imaging results, share insights, and contribute to multidisciplinary discussions regarding patient diagnosis and management.
This collaborative approach ensures that patients receive integrated care based on accurate diagnostic information.
Ensuring Patient Comfort and Safety
In addition to performing diagnostic procedures, sonographers prioritize patient comfort and safety throughout the imaging process.
They explain procedures to patients, address any concerns or questions they may have, and ensure proper positioning for optimal imaging results.
Sonographers adhere to stringent safety protocols to minimize risks associated with ultrasound technology and maintain a safe environment for both patients and themselves.
Continuing Education and Professional Development
To stay current with advancements in ultrasound technology and healthcare practices, sonographers engage in continuous education and professional development activities.
They attend workshops, conferences, and pursue certifications to enhance their skills and knowledge.
This ongoing learning enables sonographers to adapt to evolving medical technologies and provide high-quality diagnostic services to patients.
In review, sonographers play a vital role in healthcare by performing diagnostic medical sonograms, analyzing images and data, and communicating findings to the medical team.
Their expertise and dedication contribute significantly to accurate diagnoses, effective treatment planning, and patient care across various medical specialties.
As integral members of the healthcare team, sonographers uphold standards of excellence while prioritizing patient comfort and safety in their daily practice.
Read: What to Ask Your Genetic Counselor
Use of technology in sonography
Sonographers play a pivotal role in modern healthcare, leveraging cutting-edge technology to perform diagnostic imaging procedures.
They harness advanced ultrasound technology to visualize internal structures and diagnose medical conditions.
This technology utilizes high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images, offering non-invasive insights into the body’s organs and tissues.
Utilization of Ultrasound Machines
Central to a sonographer’s toolkit are ultrasound machines, sophisticated devices that emit and receive sound waves.
These machines translate the echoes produced by sound waves bouncing off bodily structures into detailed images.
Sonographers expertly manipulate these machines to obtain optimal views, adjusting settings like frequency and depth to enhance image clarity and diagnostic accuracy.
Mastery of Imaging Software
In conjunction with ultrasound machines, sonographers rely on specialized imaging software.
This software processes the raw data collected by ultrasound machines into coherent images that healthcare providers use for diagnosis.
Sonographers are trained to interpret these images, identifying abnormalities and capturing crucial details that aid in patient care and treatment planning.
Staying Current with Advancements in Technology
Sonographers must stay abreast of rapid technological advancements in their field.
Continuous professional development and training are essential as new ultrasound techniques and equipment emerge.
This includes learning about innovations such as 3D and 4D ultrasound imaging, elastography for tissue stiffness assessment, and contrast-enhanced ultrasound for vascular studies.
Embracing Technological Integration
The integration of technology in sonography extends beyond imaging capabilities.
Sonographers also utilize electronic health records (EHRs) to document findings, collaborate with healthcare teams, and ensure seamless patient care.
This digital integration enhances efficiency, accuracy, and patient safety within clinical settings.
In summary, the role of technology in modern sonography is indispensable.
From ultrasound machines and imaging software to staying current with technological advancements, sonographers play a crucial role in utilizing and advancing these technologies.
By harnessing these tools effectively, sonographers uphold standards of diagnostic excellence, contributing significantly to patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Staying proactive in adopting new technologies ensures that sonographers remain at the forefront of diagnostic imaging, driving innovation and improving healthcare delivery worldwide.
Read: Genetic Counselor vs. Geneticist: Key Differences
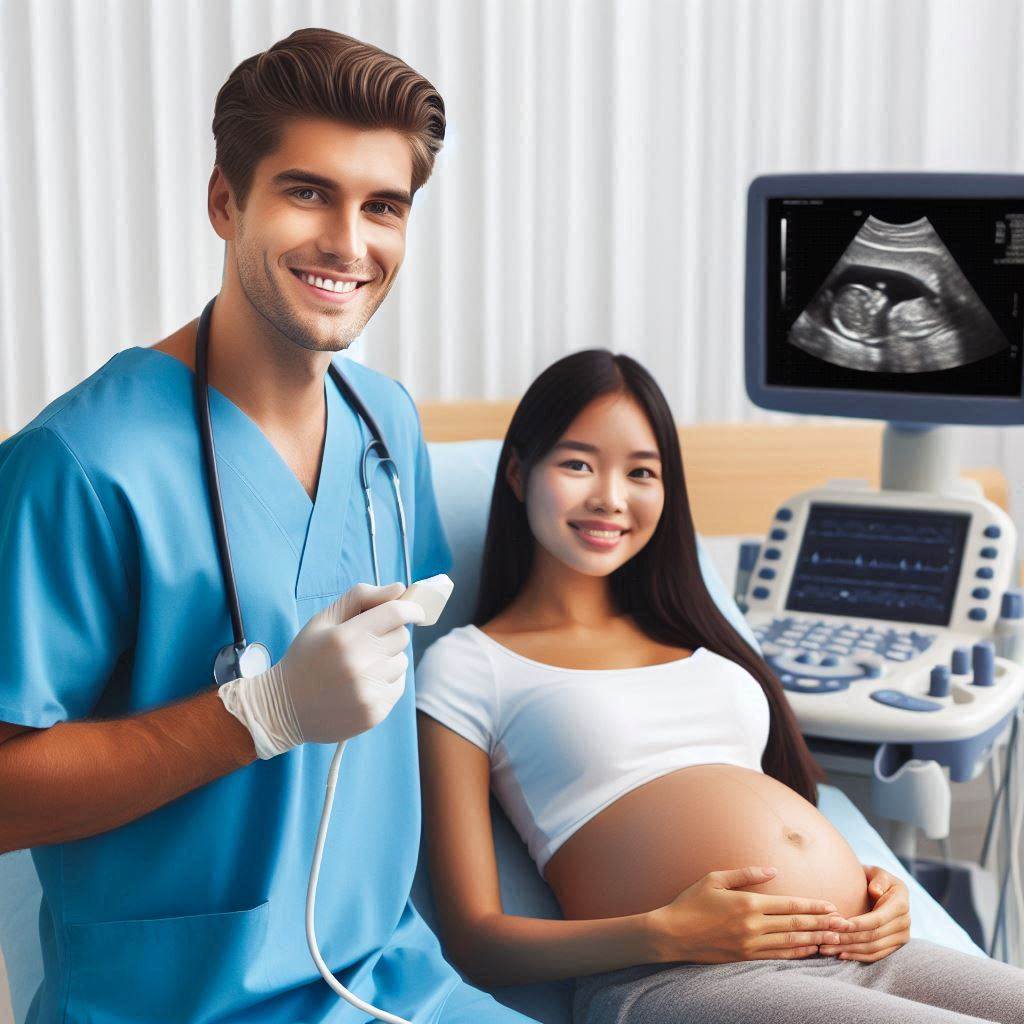
Working Environment of Sonographers
In the field of sonography, sonographers work in a variety of settings including hospitals, clinics, and private practices.
Sonographers typically work in dimly lit rooms to properly visualize images on the ultrasound machine.
They interact with patients and medical staff, explaining procedures and calming nervous individuals.
Showcase Your Business Today
Reach thousands of readers actively exploring professional services. Publish your business profile and grow your audience now.
Publish NowSonographers play a crucial role in the healthcare industry, as they aid in diagnosing and monitoring medical conditions using ultrasound technology.
Hospitals, Clinics, and Private Practices
In hospitals, sonographers may work in various departments such as obstetrics, cardiology, and radiology, performing scans on patients of all ages.
Private practices offer sonographers the opportunity to work closely with physicians in specialized areas such as musculoskeletal or vascular sonography.
Clinics may have a more fast-paced environment, requiring sonographers to perform multiple scans in a day to meet patient needs.
Interacting with Patients and Medical Staff
Interacting with patients is a key responsibility of sonographers as they explain procedures and address any concerns the individual may have.
Sonographers collaborate with medical staff to ensure the accuracy of ultrasound images and provide accurate interpretations for diagnosis.
They work closely with radiologists and physicians to deliver high-quality images that aid in the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions.
Maintaining Patient Confidentiality and Comfort during Procedures
Sonographers must prioritize patient confidentiality and ensure that all personal health information is protected in accordance with privacy laws.
During procedures, sonographers must also prioritize patient comfort, positioning them appropriately and adjusting equipment as needed for clear imaging.
They must maintain a high level of professionalism and compassion to ensure patients feel safe and secure during their ultrasound examinations.
In a nutshell, sonographers play a vital role in healthcare by using ultrasound technology to assist in the diagnosis and treatment of medical conditions across various medical settings.
Read: How Genetic Counselors Help with Rare Diseases
Gain More Insights: Pros and Cons of Being a Sleep Technologist
Challenges Faced by Sonographers
Sonographers encounter various challenges in their daily work that demand resilience and expertise.
The job involves interpreting complex medical images accurately, often under time constraints.
These professionals must navigate diverse patient needs and conditions, requiring adaptability and quick decision-making skills.
Additionally, maintaining patient comfort and safety adds another layer of responsibility to their workload.
Long Hours on Feet
A significant aspect of a sonographer’s role is the requirement to remain on their feet for extended periods.
This physical demand can lead to fatigue and discomfort, emphasizing the importance of ergonomic practices and proper footwear.
Despite these challenges, sonographers maintain focus and precision throughout their shifts to ensure accurate diagnostic imaging for patients.
Physically Demanding Work
The physical demands of sonography extend beyond standing for long hours.
Maneuvering heavy equipment and adjusting patients’ positions for optimal imaging quality are routine tasks.
This aspect of the job necessitates strength and dexterity, as well as the ability to handle repetitive motions effectively.
Sonographers prioritize patient care while managing these physical demands to deliver high-quality imaging results consistently.
High Level of Concentration Required
Sonographers must maintain a high level of concentration throughout their examinations to capture clear and detailed images.
This focus is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective communication with healthcare teams.
They must assess images in real-time, identifying abnormalities or areas needing further examination promptly.
This mental intensity underscores the importance of continuous education and staying updated with technological advancements in ultrasound technology.
In fact, the role of a sonographer encompasses more than technical skills and medical knowledge.
It requires resilience to overcome challenges, physical stamina to endure long hours on feet, and intense concentration to ensure precise imaging.
Despite the demanding nature of their work, sonographers play a crucial role in healthcare, contributing to accurate diagnoses and patient care outcomes.
Salary and Job Outlook for Sonographers
Sonographers play a crucial role in healthcare, utilizing advanced technology to produce images for medical diagnosis.
Their salaries and job outlook reflect their specialized skills and the demand in the healthcare industry.
Average Salary Range
Sonographers typically enjoy competitive salaries, reflecting their specialized training and critical role in medical imaging.
As of recent data, the average salary for sonographers ranges from $65,000 to $90,000 annually, depending on factors such as experience, location, and specialization.
Projected Job Growth in the Healthcare Industry
The job outlook for sonographers is exceptionally positive, driven by technological advancements in medical imaging and an aging population requiring more diagnostic services.
Over the next decade, the demand for diagnostic medical sonographers is projected to grow by 17%, much faster than the average for all occupations.
Understanding Sonographers’ Salaries
Sonographers’ salaries vary based on several factors, including experience, location, and specialization.
According to recent statistics, the average annual salary for sonographers falls within a broad range, highlighting their critical role and specialized skills.
Factors Influencing Salary Range
- Experience: Entry-level sonographers may start with salaries around $65,000, with potential increases based on years in the field and expertise gained.
- Location: Salaries can vary significantly by geographic region. Urban areas and states with higher costs of living typically offer higher salaries to attract skilled sonographers.
- Specialization: Sonographers specializing in areas such as cardiovascular or pediatric imaging may command higher salaries due to their advanced skills and specialized knowledge.
Job Growth Prospects for Sonographers
The demand for sonographers is expected to surge in the coming years, driven by technological advancements and the healthcare needs of an aging population.
This growth translates into excellent job prospects for individuals pursuing a career in diagnostic medical sonography.
Industry Trends Driving Growth
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in ultrasound technology continually expand the scope and accuracy of medical imaging, increasing the demand for skilled sonographers.
- Aging Population: As the population ages, there is a growing need for diagnostic procedures to detect and monitor medical conditions, further boosting the demand for sonographers.
- Healthcare Accessibility: Increased access to healthcare services, including diagnostic imaging, contributes to the steady demand for qualified sonographers across various healthcare settings.
Sonographers play a pivotal role in modern healthcare, utilizing advanced technology to provide critical diagnostic images.
With competitive salaries and robust job growth projections, pursuing a career in diagnostic medical sonography offers promising opportunities for professional growth and contribution to patient care.
As the healthcare landscape evolves, sonographers remain integral to the diagnostic process, ensuring accurate and timely medical evaluations through advanced imaging technologies.
Conclusion
The role of sonographers is pivotal in modern healthcare settings, contributing significantly to diagnostic accuracy and patient care.
Their expertise in operating ultrasound equipment and interpreting images plays a crucial role in the early detection and treatment of various medical conditions.
Recap of Key Responsibilities of Sonographers
Sonographers perform a range of critical duties, including preparing patients for procedures, operating ultrasound machines, capturing images of internal organs, and analyzing these images for abnormalities.
They collaborate closely with physicians to provide accurate diagnostic information that guides patient treatment plans.
Importance of Sonographers in Providing Quality Healthcare
Sonographers are integral to the healthcare team, supporting physicians in diagnosing conditions such as cardiovascular issues, pregnancies, and abdominal abnormalities.
Their precise imaging skills help detect diseases early, enhancing patient outcomes and reducing the need for invasive procedures.
Encouragement for Those Interested in Pursuing a Career in Sonography
For those considering a career in sonography, it offers a dynamic and rewarding path in healthcare.
With advancements in technology, the field continues to evolve, offering opportunities for specialization and professional growth.
Sonographers enjoy a fulfilling role where their skills directly impact patient well-being, making a difference in healthcare delivery.
Sonography demands dedication to continuous learning and staying updated with technological advancements.
It requires strong communication skills to interact with patients and medical teams effectively.
Despite the physically demanding nature of the job, the fulfillment of contributing to better patient outcomes makes it a gratifying career choice.
Final Thoughts
In closing, sonographers play a crucial role in healthcare by providing accurate diagnostic imaging that supports timely and effective patient care.
Their expertise and commitment ensure that medical teams have essential information for diagnosing and treating a wide range of conditions.
For those interested in pursuing this career path, it promises both professional satisfaction and opportunities for growth in a dynamic healthcare environment.
[E-Books for Sale]
The Big Book of 500 High-Paying Jobs in America: Unlock Your Earning Potential
$19.99 • 500 High-Paying Jobs • 330 pages
Explore 500 high-paying jobs in America and learn how to boost your career, earn more, and achieve success!
See All 500 High-Paying Jobs of this E-Book
1001 Professions Without a Degree: High-Paying American Jobs You Can Start Now
$19.99 • 1001 Professions Without a Degree • 174 pages
Discover 1001 high-paying jobs without a degree! Unlock career tips, skills, and success strategies for just $19.99!