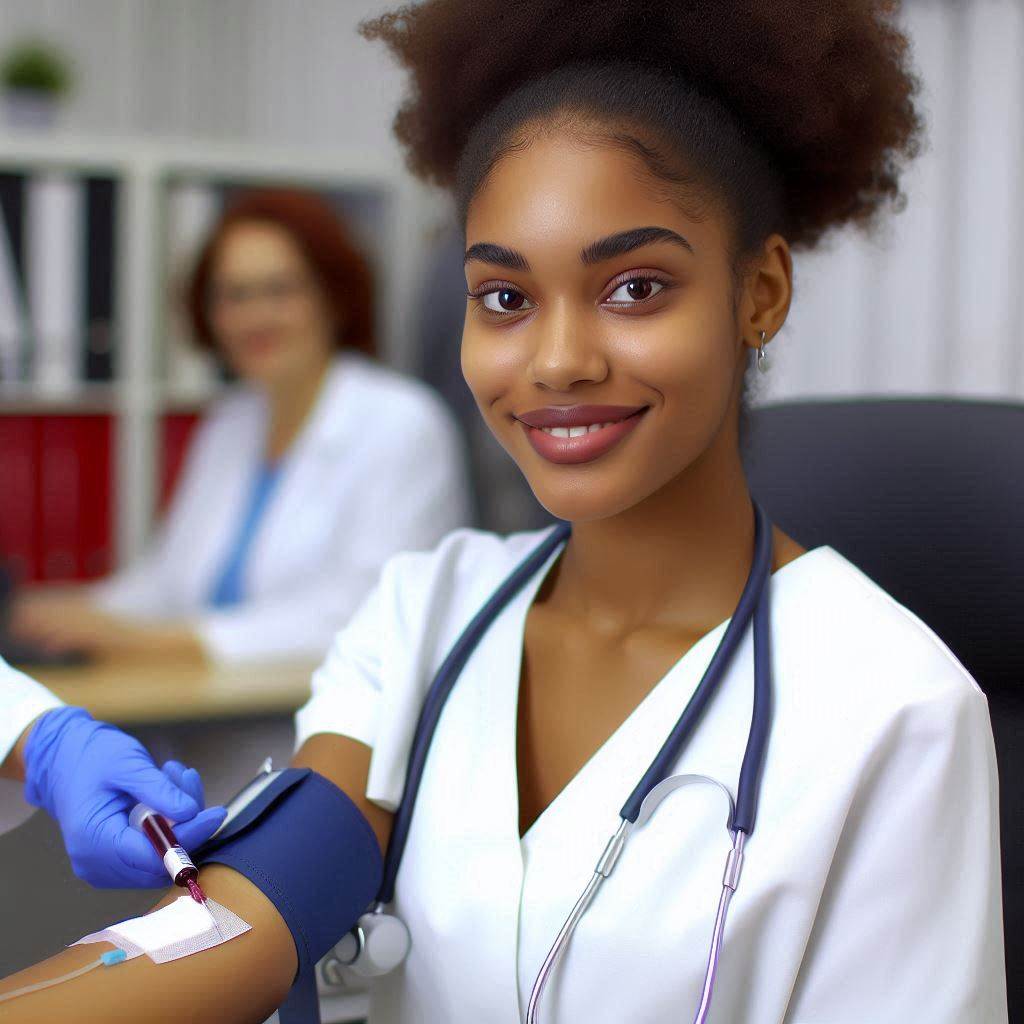
Introduction
Safe and effective blood draws are essential for accurate medical diagnoses. Proper technique minimizes patient discomfort and ensures reliable test results.
Blood draws, when done incorrectly, can lead to complications.
These include infections, bruising, and significant pain. Infection risk increases with improper needle handling and lack of sterilization.
Bruising occurs when veins are missed or punctured multiple times. Pain results from poor technique and patient anxiety.
Following best practices mitigates these risks and enhances patient experience. Sterilize the area before inserting the needle to prevent infections.
Use a gentle touch to find the vein and avoid unnecessary punctures. Communicate with the patient to ease their anxiety and ensure their comfort.
Proper training and adherence to protocols are crucial for healthcare professionals performing blood draws.
Incorrect blood draws can also lead to inaccurate test results. Contaminated samples may give false readings, impacting diagnosis and treatment plans.
Hemolysis, or the destruction of red blood cells, occurs with improper technique. This affects the sample’s integrity and can lead to repeat procedures.
By emphasizing safety and effectiveness, healthcare professionals can improve patient outcomes.
This includes using the correct gauge needle and applying appropriate pressure post-draw.
Monitoring patient reactions and addressing concerns immediately enhances the process.
Educating patients about the procedure helps reduce fear and builds trust.
In summary, safe and effective blood draws are vital. They prevent complications, ensure accurate results, and enhance patient trust and comfort.
Proper technique, sterilization, and patient communication are key components. Prioritizing these practices ensures the best possible care for patients.
Selecting and preparing the right equipment
When it comes to safe and effective blood draws, selecting and preparing the right equipment is crucial to ensure accurate results and prevent infections.
Sterile needles and equipment are essential for blood draws to prevent the risk of contamination and reduce the chances of infection.
Always check the expiration date and integrity of the needles and syringes to guarantee their effectiveness and avoid any complications during the procedure.
Use disposable tourniquets, alcohol swabs, and gauze pads to maintain a clean and hygienic environment for the blood draw process.
The importance of using sterile needles and equipment
Sterile equipment helps reduce the risk of introducing pathogens into the bloodstream, which can lead to serious infections or complications for the patient.
Transform Your Career Today
Unlock a personalized career strategy that drives real results. Get tailored advice and a roadmap designed just for you.
Start NowProperly sterilized needles and equipment also ensure the accuracy of the blood sample collected, allowing for reliable test results and proper diagnosis.
By using sterile needles and equipment, healthcare providers demonstrate their commitment to patient safety and quality care, building trust with patients.
How to properly clean and prepare the skin before drawing blood
Start by washing your hands thoroughly with soap and water to prevent the spread of germs and ensure a sterile environment for the blood draw.
Put on disposable gloves to protect yourself and the patient from potential contamination during the blood draw procedure.
Wipe the skin with an alcohol swab in a circular motion to clean the area where the needle will be inserted, ensuring it is free from dirt and bacteria.
Allow the skin to air dry completely before proceeding with the blood draw to prevent any stinging sensation or discomfort for the patient.
Use a sterile needle to perform the blood draw, following the correct technique and guidelines to minimize pain and the risk of complications.
By following these best practices for safe and effective blood draws, healthcare providers can ensure the well-being of their patients and maintain high standards of quality care.
Read: Physician Assistant Role in Primary Care: Vital Functions
Ensuring patient comfort and safety
When performing a blood draw, it is essential to prioritize the patient’s comfort and safety.
Explain the Procedure Thoroughly
- Before starting the blood draw, take the time to explain the procedure to the patient.
- Make sure they understand what will happen and why it is necessary.
- Answer any questions or address any concerns they may have.
- This helps alleviate anxiety and build trust between the patient and the healthcare provider.
Use Techniques to Minimize Pain and Discomfort
- There are several techniques that can help minimize pain and discomfort during a blood draw.
- Selecting the right needle size based on the patient’s vein size can reduce pain.
- Ensuring the tourniquet is not too tight can prevent unnecessary discomfort.
- Using a numbing cream or spray on the area can help numb the skin before the procedure.
- Applying gentle pressure at the injection site after the draw can reduce bruising and soreness.
Positioning the Patient Comfortably
- Positioning the patient correctly can make a significant difference in their comfort during the blood draw.
- Ensure the patient is sitting or lying down in a relaxed position.
- Keep their arm supported at heart level to help with blood flow and ease of access to the vein.
- Provide a pillow or cushion for extra support and comfort.
Engage in Calming Techniques
- Using calming techniques can help the patient relax and reduce anxiety during the blood draw.
- Encourage deep breathing exercises before and during the procedure.
- Engage in conversation to distract the patient and create a more comfortable environment.
- Offer a stress ball or something for the patient to hold onto to ease tension.
Monitor the Patient’s Well-being
- Throughout the blood draw, it’s crucial to monitor the patient’s well-being and comfort.
- Check in with them regularly to see how they are feeling.
- Be prepared to pause or stop the procedure if the patient is experiencing significant pain or distress.
- Offer support and reassurance throughout the process.
Provide Adequate Post-Procedure Care
- After the blood draw is complete, provide the patient with information on post-procedure care.
- Advise them to keep the bandage on for a specific amount of time.
- Instruct them to avoid heavy lifting or strenuous activities with the arm that was used for the blood draw.
- Remind them to drink plenty of water to help replenish lost fluids.
In fact, prioritizing patient comfort and safety during a blood draw is crucial for a positive experience.
By explaining the procedure, using techniques to minimize pain and discomfort, and providing adequate care before and after the draw, healthcare providers can ensure a smooth and successful blood draw while maintaining the patient’s well-being.
Read: Common Challenges Faced by Phlebotomists at Work
Identifying and labeling specimens correctly
In the medical field, it is crucial to identify and label blood samples accurately. This practice ensures patient safety, quality of care, and reliable test results.
Importance of labeling blood samples accurately
- Prevents errors: Labeling ensures that the right sample belongs to the right patient.
- Track and trace: Proper labeling helps in tracking the specimen throughout the testing process.
- Compliance: Accurate labeling is essential to meet regulatory requirements and standards.
- Communication: Clear labeling facilitates effective communication among healthcare providers.
- Quality control: Properly labeled samples contribute to the accuracy of test results.
Potential consequences of mislabeling specimens
- Misdiagnosis: Incorrect labels can lead to misinterpretation of test results and wrong diagnosis.
- Treatment errors: Mislabeling may result in patients receiving the wrong treatment or medication.
- Patient harm: Misidentification can cause harm to patients, compromising their health and safety.
- Legal implications: Mislabeling can lead to legal issues, liability, and loss of trust in healthcare providers.
- Costly mistakes: Errors in labeling can result in unnecessary repeat tests, delays in treatment, and increased healthcare costs.
Overall, proper identification and accurate labeling of blood samples are fundamental best practices in healthcare settings.
It is essential for healthcare professionals to emphasize the importance of this process and follow protocols diligently to ensure patient safety and quality care.
Read: Benefits of Seeing a Mental Health Counselor

Proper technique for venipuncture
Steps involved in performing a successful venipuncture
Performing a venipuncture requires proper technique to ensure a safe and effective blood draw.
Here are the steps involved in performing a successful venipuncture:
- Prepare the Patient: Explain the procedure to the patient and obtain their consent.
Ensure the patient is comfortable and seated or lying down before beginning the procedure. - Gather Supplies: Collect all necessary supplies including a tourniquet, alcohol swab, gauze, bandage, and the appropriate needle for the blood draw.
- Locate Veins: Use proper lighting to identify suitable veins for venipuncture. Feel for veins that are straight, firm, and easily palpable.
- Apply Tourniquet: Place the tourniquet 3-4 inches above the intended venipuncture site.
The purpose of the tourniquet is to engorge the veins for easy visibility. - Clean the Site: Ensure the venipuncture site is cleaned with an alcohol swab in a circular motion starting from the center and moving outward.
- Needle Insertion: Hold the needle at a 15-30 degree angle and insert it into the vein with a swift and steady motion. Be careful not to go through the vein.
- Blood Collection: Once the needle is inserted correctly, blood will start to flow into the collection tube. Monitor the flow and adjust if needed.
- Remove Needle: Once an adequate amount of blood is collected, remove the needle gently and apply pressure to the site with gauze. Secure with a bandage.
- Post-Procedure Care: Dispose of the needle in a sharps container, label the blood samples correctly, and provide post-procedure care instructions to the patient.
Tips for Locating Veins and Inserting the Needle Correctly
Proper technique is crucial for a successful venipuncture. Here are some tips to help you locate veins and insert the needle correctly:
Transform Your Career Today
Unlock a personalized career strategy that drives real results. Get tailored advice and a roadmap designed just for you.
Start Now- Use Proper Lighting: Good lighting is essential for identifying veins. Position the light source above the patient’s arm to illuminate the veins.
- Feel for Veins: Use your fingers to gently palpate the veins to determine their size, depth, and location. Choose veins that are easily visible and palpable.
- Anchor the Vein: To stabilize the vein and prevent it from rolling, anchor the vein by applying gentle traction below the intended puncture site.
- Insert the Needle Correctly: Ensure the bevel of the needle is facing up during insertion. Insert the needle smoothly and avoid moving it once it is in the vein.
- Monitor Blood Flow: Once the needle is inserted, monitor the blood flow and adjust the angle if needed to ensure a steady flow of blood into the collection tube.
- Communicate with the Patient: Communicate with the patient throughout the procedure to help alleviate anxiety and discomfort. Inform them of any sensations they may feel.
- Practice Makes Perfect: Venipuncture is a skill that improves with practice. As you gain experience, you will become more confident in your technique and accuracy.
- Seek Feedback: Don’t hesitate to seek feedback from experienced phlebotomists or healthcare professionals to improve your technique and learn new tips and tricks.
By following these steps and tips, you can ensure a safe and effective blood draw for your patients.
Remember to always prioritize patient safety and comfort during venipuncture procedures.
Read: Day in the Life of a Mental Health Counselor
Handling and disposing of biohazardous materials
When it comes to handling and disposing of biohazardous materials in the context of blood draws, it is crucial to follow strict protocols to ensure the safety of both healthcare practitioners and patients.
Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Proper Disposal of Used Needles and Blood Samples
- Immediately after use, needles should be properly disposed of in designated sharps containers.
- These containers should be puncture-proof and leak-resistant to prevent accidental needle sticks.
- Used blood samples should be placed in biohazard bags or containers labeled with the biohazard symbol.
- Do not recap needles after use to minimize the risk of needle-stick injuries.
- Dispose of biohazard bags or containers according to facility guidelines and regulations.
Following Proper Biohazard Waste Management Practices
- Adhere to established protocols for handling biohazardous materials to prevent contamination.
- Know the location of designated waste disposal areas and containers in the healthcare facility.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling biohazardous waste.
- Regularly inspect and replace sharps containers to prevent overfilling and spills.
- Train healthcare staff on proper disposal procedures and the importance of adhering to guidelines.
By following these best practices for the safe and effective disposal of biohazardous materials, healthcare providers can minimize the risk of exposure to infectious agents and uphold the highest standards of patient care.
Conclusion
Safe and effective blood draws are essential for patient safety.
Remember to always properly identify the patient before starting the procedure.
Use the correct equipment and follow sterile techniques to prevent infections.
Properly dispose of needles and sharps to prevent accidental injuries.
Be sure to communicate with patients to alleviate any anxiety or discomfort.
Continuous training and education on best practices are crucial for healthcare professionals.
By prioritizing safe and effective blood draws, healthcare professionals can ensure the well-being of their patients.
[E-Books for Sale]
The Big Book of 500 High-Paying Jobs in America: Unlock Your Earning Potential
$19.99 • 500 High-Paying Jobs • 330 pages
Explore 500 high-paying jobs in America and learn how to boost your career, earn more, and achieve success!
See All 500 High-Paying Jobs of this E-Book
1001 Professions Without a Degree: High-Paying American Jobs You Can Start Now
$19.99 • 1001 Professions Without a Degree • 174 pages
Discover 1001 high-paying jobs without a degree! Unlock career tips, skills, and success strategies for just $19.99!