Introduction
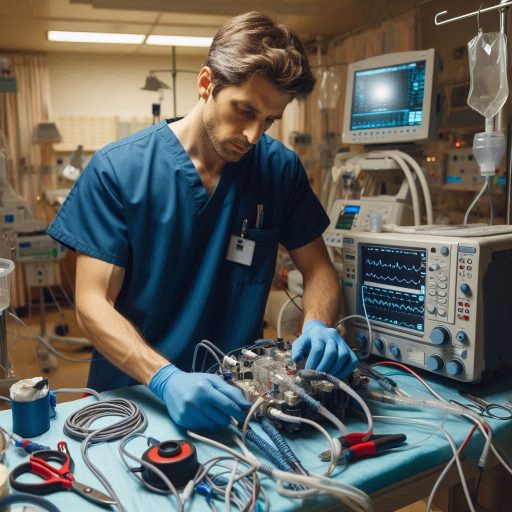
Biomedical technicians are essential in maintaining and repairing medical equipment used in healthcare settings.
Their work ensures that devices like infusion pumps, defibrillators, and imaging machines operate safely and effectively.
To perform their tasks, technicians rely on a variety of specialized tools and technologies.
Key tools include oscilloscopes, which help diagnose electrical issues, and multimeters, used to measure voltage and current.
Calibrators ensure medical devices provide accurate readings, crucial for patient safety.
Diagnostic software helps technicians troubleshoot complex problems and update device firmware.
These tools enable technicians to perform precise repairs and routine maintenance, ensuring optimal performance of medical equipment.
Advanced technologies, such as computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS), streamline work orders and track equipment status.
These systems enhance efficiency by organizing data and scheduling tasks effectively.
The integration of these technologies supports technicians in managing their workload and improving response times.
Overall, the effectiveness of biomedical technicians hinges on the tools and technologies they use.
These instruments not only facilitate accurate repairs and maintenance but also contribute to the overall quality of patient care.
Investing in the right tools and technologies ensures technicians can perform their roles efficiently and maintain high standards in healthcare settings.
Types of Tools Used by Biomedical Technicians
Biomedical technicians rely on a variety of tools to maintain and repair medical equipment.
Each tool serves a specific purpose, ensuring that devices operate safely and effectively.
Diagnostic Equipment
Diagnostic equipment allows biomedical technicians (BMETs) to identify issues with medical devices.
Multimeters measure electrical parameters like voltage, current, and resistance.
Oscilloscopes help visualize electronic signals, enabling technicians to analyze waveforms.
Electrical safety analyzers test equipment for electrical safety and grounding issues.
These tools help BMETs diagnose problems accurately and quickly.
Repair Tools
Repair tools are essential for fixing malfunctioning medical devices.
Screwdrivers and wrenches allow technicians to disassemble and reassemble equipment.
Soldering irons are used for making precise electronic repairs on circuit boards.
Pliers and wire cutters assist in handling and cutting wires.
A portable toolkit often contains a variety of these tools, ensuring BMETs can address different issues on-site.
Additionally, thermal cameras can detect overheating components, providing another layer of diagnostic capability.
Calibration Devices
Calibration devices ensure that medical equipment functions within the required specifications.
Tools include test sets designed for specific types of equipment, such as infusion pumps or imaging machines.
For example, a calibration tester for blood glucose meters checks accuracy and reliability.
Pressure gauges and flow meters are used for calibrating devices that measure or deliver fluids.
Accurate calibration is crucial for maintaining the integrity and performance of medical devices.
Testing Devices
Testing devices help BMETs verify that equipment performs as intended after repairs or maintenance.
Electrical test simulators mimic patient conditions to ensure devices respond correctly.
Signal generators produce various types of signals to test equipment responses.
Leakage current testers measure any unwanted electrical currents that could pose safety risks.
Insulation testers check the integrity of electrical insulation, preventing potential shocks or equipment failure.
These devices are vital for validating that medical equipment meets safety and operational standards.
In summary, BMETs use a range of specialized tools to maintain, repair, and calibrate medical equipment.
Diagnostic equipment helps in identifying issues, while repair tools facilitate the actual fixing process.
Calibration devices ensure accuracy and compliance with specifications, and testing devices confirm that equipment functions correctly.
Each tool plays a crucial role in the efficient and effective operation of medical devices, ensuring that they meet safety and performance standards.
Technology Trends in Biomedical Technician Tools
Use of Electronic Health Records
Biomedical Technicians (BMETs) use Electronic Health Records (EHRs) to streamline their work.
EHRs provide real-time data on medical devices and patient histories.
These records enable BMETs to track device performance and address issues promptly.
By accessing patient information quickly, BMETs can ensure that medical equipment functions correctly according to patient needs.
EHRs also allow for better coordination with healthcare providers, improving overall patient care.
Real-time updates help BMETs make informed decisions about equipment maintenance and repairs.
Remote Monitoring Devices
Remote monitoring devices are becoming crucial in biomedical technology.
These devices collect data from medical equipment and transmit it to BMETs from a distance.
Remote monitoring allows BMETs to oversee equipment performance without being physically present.
This capability enables them to detect and address issues before they become critical.
Remote diagnostics can reduce response times and improve patient outcomes.
BMETs can analyze data trends and predict potential problems, making maintenance more proactive.
Wireless Communication Tools
Wireless communication tools are essential for modern BMETs.
These tools facilitate quick and efficient communication between BMETs and healthcare staff.
Wireless systems include radios, mobile phones, and tablets that BMETs use to share information in real-time.
Instant communication ensures that BMETs receive immediate feedback on equipment performance and patient conditions.
Wireless tools also support collaboration among BMETs, enabling them to solve complex issues more effectively.
The use of wireless technology streamlines workflows and enhances the coordination of maintenance tasks.
Predictive Maintenance Software
Predictive maintenance software helps BMETs anticipate equipment failures before they occur.
This software analyzes data collected from medical devices to identify patterns and potential issues.
By predicting failures, BMETs can perform maintenance tasks at optimal times, preventing unexpected breakdowns.
Predictive maintenance improves equipment reliability and extends its lifespan.
It also helps BMETs manage their workload more efficiently by scheduling maintenance during non-peak hours.
This proactive approach minimizes equipment downtime and ensures continuous patient care.
Read: Networking Tips for Surveying and Mapping Professionals
Training required for using biomedical technician tools
Certification Programs
Certification programs play a crucial role in the career development of Biomedical Equipment Technicians.
They validate a technician‘s skills and knowledge in handling complex medical equipment.
Many programs, such as those offered by the Association for the Advancement of Medical Instrumentation (AAMI), cover a wide range of topics.
These include safety standards, maintenance protocols, and troubleshooting techniques.
Obtaining certification demonstrates a technician‘s commitment to their profession and enhances their employability.
It also ensures that they are up-to-date with industry standards and practices.
On-the-Job Training
On-the-job training is essential for Biomedical Equipment Technicians.
It provides hands-on experience with real-world scenarios and equipment.
This type of training allows technicians to apply theoretical knowledge in practical settings.
They learn to handle various devices, diagnose issues, and perform repairs.
Experienced mentors and supervisors often guide new technicians through this process.
This training not only improves their technical skills but also helps them understand workplace dynamics and safety protocols.
Continuing Education Courses
Continuing education courses are vital for maintaining and advancing skills in the biomedical field.
Technology in medical equipment evolves rapidly, making ongoing learning necessary.
These courses offer updates on new technologies, regulations, and best practices.
Technicians can choose courses based on their areas of interest or emerging trends.
Continuing education helps technicians stay current and competitive in their field.
It also provides opportunities for career advancement and specialization.
Manufacturer-Specific Training
Manufacturer-specific training is designed to provide in-depth knowledge about particular brands and models of medical equipment.
This training is often provided by the equipment manufacturers themselves.
Technicians learn about the unique features, maintenance requirements, and troubleshooting procedures for specific devices.
This specialized training ensures that technicians can effectively manage and repair equipment from various manufacturers.
It also helps in understanding warranty and service agreements, which are crucial for maintaining high-quality service.
Read: Field vs. Office Work in Surveying and Mapping
Safety protocols for handling tools and technologies
Proper Equipment Maintenance
Maintaining biomedical equipment properly is crucial for safety and functionality.
Biomedical technicians (BMETs) ensure that medical devices perform accurately and reliably.
Regular maintenance prevents unexpected failures and prolongs the life of the equipment.
Technicians follow detailed manufacturer guidelines to perform this maintenance effectively.
They perform routine checks, calibrations, and repairs according to these instructions.
This adherence guarantees that the equipment meets safety and performance standards.
Technicians also need to stay updated on maintenance procedures.
Manufacturers occasionally release updates or revisions to maintenance protocols.
BMETs must review these updates to ensure compliance with the latest standards.
Failure to follow current guidelines can lead to equipment malfunctions, endangering patient safety.
Following Manufacturer Guidelines
Following manufacturer guidelines is fundamental to proper equipment maintenance.
Each medical device comes with specific instructions on how to maintain it.
These guidelines include procedures for cleaning, calibrating, and inspecting equipment.
Deviating from these instructions can lead to equipment failure or inaccurate test results.
BMETs must thoroughly read and understand these guidelines.
They should use the recommended tools and follow prescribed procedures.
Additionally, BMETs should document all maintenance activities as outlined by the manufacturer.
This documentation helps track the equipment’s service history and ensures compliance with safety standards.
Using Personal Protective Equipment
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is essential for BMETs while performing maintenance tasks.
PPE includes gloves, masks, goggles, and lab coats.
Wearing appropriate PPE protects technicians from exposure to harmful substances and electrical hazards.
It also ensures that the equipment remains uncontaminated during maintenance.
BMETs should always inspect their PPE for damage before use.
They must replace any worn or damaged equipment immediately.
Proper training on the use of PPE is also crucial.
This training ensures that BMETs understand how to use and dispose of PPE correctly, maintaining a safe working environment.
Reporting Safety Incidents
Reporting safety incidents is a critical responsibility for BMETs.
If an incident occurs, such as equipment malfunction or exposure to hazardous materials, technicians must report it immediately.
Prompt reporting allows for quick assessment and mitigation of risks.
It also helps in preventing future incidents by identifying underlying issues.
BMETs should follow established protocols for incident reporting.
This usually involves documenting the incident details and notifying relevant personnel.
Reporting helps in improving safety procedures and ensuring compliance with safety regulations.
By addressing and learning from safety incidents, BMETs contribute to a safer and more efficient work environment.
By adhering to proper maintenance procedures, following manufacturer guidelines, using PPE, and reporting safety incidents.
BMETs play a vital role in ensuring the safety and reliability of biomedical equipment.
These practices help maintain high standards of patient care and operational efficiency in healthcare settings.
Transform Your Career Today
Unlock a personalized career strategy that drives real results. Get tailored advice and a roadmap designed just for you.
Start NowRead: Importance of Accuracy in Surveying and Mapping
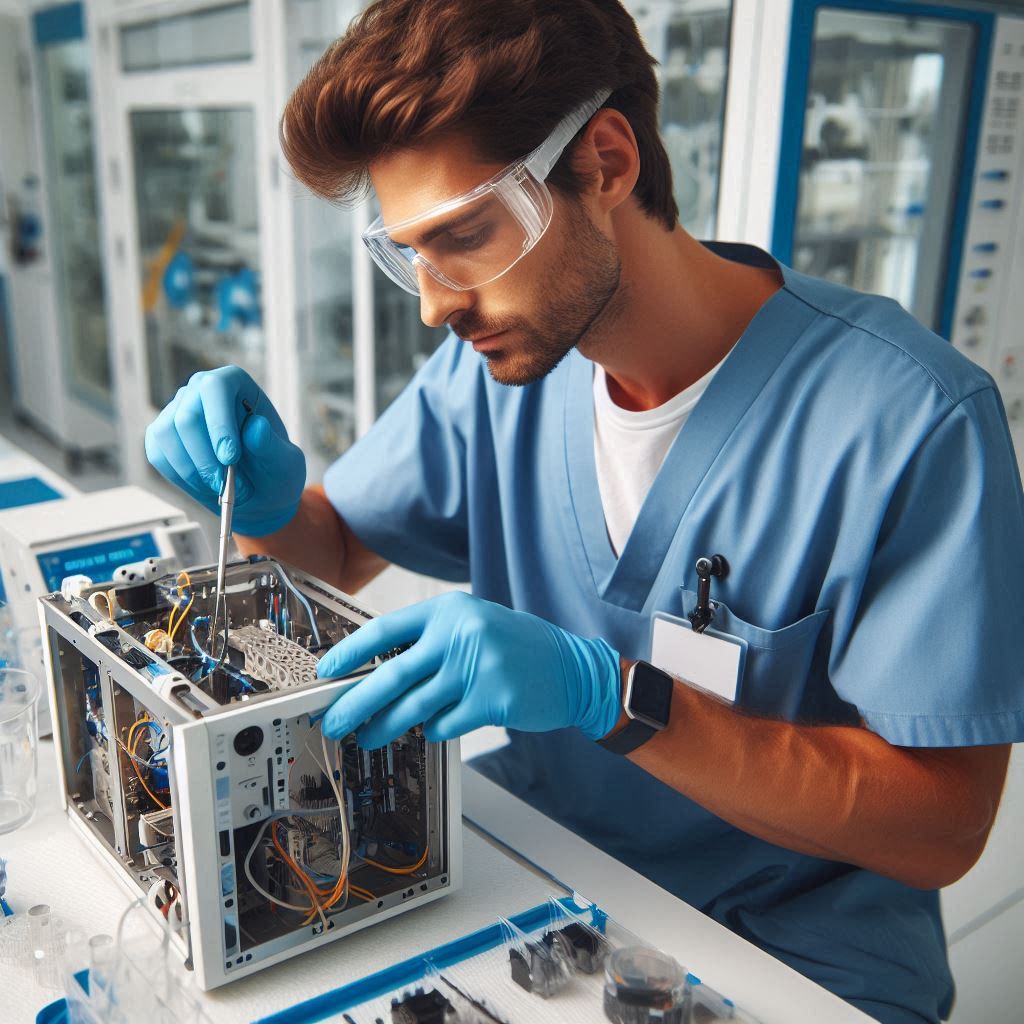

Challenges Faced by Biomedical Technicians in Using Tools
Complex Equipment Interfaces
Biomedical technicians frequently work with sophisticated medical equipment featuring complex interfaces.
Modern medical devices often include advanced touchscreens, digital controls, and integrated software.
Mastering these interfaces requires both technical knowledge and hands-on experience.
BMETs must understand device menus, settings, and diagnostic tools to operate them effectively.
These interfaces can vary significantly between manufacturers, adding complexity to their tasks.
Training programs and manuals help technicians navigate these advanced interfaces.
Simulations and interactive tutorials are often used to familiarize BMETs with new equipment.
Staying proficient with these interfaces is crucial for accurate operation and troubleshooting.
As technology evolves, BMETs must continually update their skills to keep pace with new device features and functionalities.
Troubleshooting Technical Issues
Troubleshooting technical issues is a core responsibility for biomedical technicians.
Diagnosing and resolving problems with medical devices demands a systematic approach.
BMETs use diagnostic tools, such as oscilloscopes and multimeters, to identify faults.
Detailed knowledge of device schematics and error codes is essential for effective troubleshooting.
When a device malfunctions, BMETs must follow a structured process.
They start by reviewing the device‘s history, recent repairs, and any error messages.
Next, they test the equipment using diagnostic tools and consult technical manuals.
Once the issue is identified, technicians perform repairs or replacements as needed.
Effective troubleshooting ensures devices remain operational and safe for patient use.
Keeping Up with Rapidly Evolving Technology
Biomedical technology advances at a rapid pace, presenting challenges for BMETs.
New devices and technologies emerge frequently, requiring technicians to stay informed.
BMETs must engage in ongoing education to remain knowledgeable about the latest advancements.
This can include attending industry conferences, taking online courses, and reading technical journals.
Keeping up with evolving technology also means adapting to new maintenance and calibration techniques.
Technicians need to learn how to handle updated equipment and software.
Continuous learning ensures BMETs can manage and repair the latest medical devices effectively.
Staying current with technology helps maintain the quality and safety of patient care.
Budget Constraints for Equipment Purchases
Budget constraints often impact the purchase and maintenance of medical equipment.
Healthcare facilities must balance the cost of acquiring new devices with available funds.
Limited budgets can lead to challenges in obtaining the latest technology or upgrading existing equipment.
BMETs play a critical role in managing these constraints.
They help prioritize equipment needs based on functionality and patient impact.
Technicians often work with procurement teams to select cost-effective solutions that meet operational requirements.
Effective maintenance of existing equipment can also extend its lifespan, reducing the need for frequent replacements.
Read: Surveying and Mapping Technician: Job Satisfaction
Explore Further: Historical Milestones in Petroleum Engineering
Advantages of using advanced tools and technologies
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
Biomedical Technicians (BMETs use advanced tools and technologies to enhance diagnostic accuracy.
Modern diagnostic equipment like MRI machines, CT scanners, and ultrasound devices offer high-resolution imaging.
These tools enable precise detection of medical conditions and abnormalities.
Accurate diagnostics are crucial for timely and effective treatment.
For instance, advanced imaging technologies can detect issues that older models might miss.
BMETs ensure these tools are calibrated and maintained to provide the most reliable results.
By leveraging cutting-edge technology, BMETs contribute significantly to accurate diagnoses, which is vital for patient outcomes.
Faster Repair Times
Technology advancements also impact repair times for medical equipment.
BMETs use sophisticated diagnostic tools like handheld analyzers and software-based troubleshooting systems.
These tools streamline the repair process by quickly identifying faults.
Automated diagnostic systems provide real-time data, which speeds up repairs and reduces downtime.
Faster repairs mean that essential medical equipment is back in service more quickly.
This efficiency helps healthcare facilities maintain continuous operations and avoid disruptions in patient care.
Technicians can swiftly address issues, ensuring that medical equipment remains functional and available when needed.
Enhanced Patient Care
The integration of advanced tools and technologies directly improves patient care.
BMETs play a key role in maintaining the reliability of medical devices.
Technologies such as remote monitoring systems allow for continuous tracking of patient conditions.
This constant monitoring enables early intervention if problems arise.
Enhanced diagnostic tools lead to more accurate treatment plans, which directly benefit patient outcomes.
Reliable equipment ensures that patients receive timely and appropriate care.
Additionally, well-maintained devices reduce the risk of malfunctions that could negatively impact patient safety.
Cost Savings for Healthcare Facilities
Advanced tools and technologies can lead to significant cost savings for healthcare facilities.
High-quality diagnostic equipment reduces the need for repeat tests, lowering overall costs.
Faster repair times mean less downtime for expensive medical equipment, avoiding costly delays.
Efficient maintenance practices extend the lifespan of devices, reducing the frequency of costly replacements.
Investing in modern technology often results in better long-term financial outcomes for healthcare facilities.
Moreover, accurate diagnostics and reliable equipment contribute to fewer complications, which can further lower healthcare costs.
Collaboration with other healthcare professionals
Working with Doctors and Nurses
Biomedical Technicians (BMETs work closely with doctors and nurses to ensure optimal use of medical equipment.
They collaborate to understand the specific needs of medical professionals.
Regular interactions with healthcare staff help BMETs grasp the critical functions of equipment in patient care.
This teamwork ensures that devices meet the practical demands of clinical settings.
BMETs address any issues that arise and make necessary adjustments.
Their role is crucial in maintaining the efficiency of equipment used daily by doctors and nurses.
Communicating Equipment Needs
Effective communication is essential for BMETs when discussing equipment needs with medical staff.
They must clearly articulate technical requirements and functionality.
BMETs often provide updates on new equipment, changes, or repairs.
They also discuss the implications of these changes for clinical workflows.
Transparent communication helps ensure that doctors and nurses are aware of the capabilities and limitations of the equipment.
This dialogue prevents misunderstandings and helps align equipment use with patient care goals.
Providing Technical Support
BMETs offer critical technical support to healthcare professionals.
They troubleshoot problems with medical devices and provide on-the-spot solutions.
When equipment malfunctions, BMETs quickly diagnose and repair issues to minimize disruptions.
They also train medical staff on proper equipment usage and maintenance.
By providing this support, BMETs help ensure that medical devices function correctly and efficiently.
Their expertise is vital for the smooth operation of medical technologies in patient care.
Sharing Knowledge About New Technologies
BMETs play a key role in introducing new technologies to healthcare teams.
They stay informed about the latest advancements in medical equipment.
When new technologies are implemented, BMETs educate doctors and nurses on their use.
They explain the benefits and features of new devices and how they improve patient care.
Sharing knowledge about emerging technologies helps healthcare professionals stay current with innovations.
This education ensures that new tools are integrated effectively into clinical practice.
Conclusion
Biomedical Technicians (BMETs) rely heavily on advanced tools and technologies to ensure the proper functioning of medical equipment.
Precision diagnostic devices and efficient repair tools are crucial for maintaining high standards in healthcare delivery.
These technologies allow BMETs to swiftly diagnose and address issues, thereby improving patient care and safety.
To stay effective in their roles, BMETs must continuously update their knowledge of emerging tools and technologies.
Keeping current with advancements through regular training and education is essential for maintaining equipment effectiveness and addressing new challenges.
This ongoing learning helps BMETs refine their skills and adapt to new developments in the field.
The critical role of BMETs in the healthcare system cannot be overstated.
They ensure that medical devices operate correctly, which directly impacts patient treatment outcomes and overall safety.
Their expertise in managing and maintaining equipment supports the smooth functioning of healthcare services.
Without their dedication and technical skills, the reliability and functionality of essential medical technologies would be compromised.
Ultimately affecting patient care and the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
[E-Books for Sale]
The Big Book of 500 High-Paying Jobs in America: Unlock Your Earning Potential
$19.99 • 500 High-Paying Jobs • 330 pages
Explore 500 high-paying jobs in America and learn how to boost your career, earn more, and achieve success!
See All 500 High-Paying Jobs of this E-Book
1001 Professions Without a Degree: High-Paying American Jobs You Can Start Now
$19.99 • 1001 Professions Without a Degree • 174 pages
Discover 1001 high-paying jobs without a degree! Unlock career tips, skills, and success strategies for just $19.99!